
September 27, 2023 | Revolving Door Project Newsletter
New Watchdog Reports Highlight Insufficient EPA Enforcement Ahead Of Shutdown
Corporate greed and emaciated federal regulatory capacity means people are needlessly suffering physically, and sometimes even dying. That’s the upshot of two recent reports from the EPA’s Office of the Inspector General (OIG). These reports illustrate the concerning state of environmental regulation and enforcement in regards to water quality and refinery emissions.

August 16, 2023 | Revolving Door Project Newsletter
Toni Aguilar Rosenthal Hannah Story Brown
Newsletter Confirmations CrisisGovernanceGovernment Capacity
Delayed Confirmation of Biden Nominees Both Common and Costly
On July 25, 2023, military leaders in Niger, along with members of the Presidential Guard, enacted a coup against President Mohamed Bazoum. Led by General Abdourahamane Tchiani, a Nigerien military officer and self-appointed President of Niger’s military junta, coup plotters detained the democratically-elected President Bazoum, as well as members of his family, threatened to kill him in the event of any military intervention in the coup, and most recently put him on trial for treason.
Despite widespread rumors of an emergent coup in the country, the United States was reportedly “blindsided” by it, and scrambled to respond. Of course, American intel regarding the actual political atmosphere of the country was hindered in no small way by the lack of State Department personnel staffing embassies in the region.

August 09, 2023
The Small Business Administration Needs To Increase Its Capacity, Not Lending Authority To Fintechs
Continued reliance on underregulated financial technology companies could stand to further harm the agency’s reputation and goals for lending equity.
August 02, 2023 | Revolving Door Project Newsletter
Following Failed Hearing, Jim Jordan And Republicans Try New Tacks To Take Down Khan and Kanter
Two weeks ago, Federal Trade Commission (FTC) Chair Lina Khan entered a House Judiciary Committee hearing with a target on her back. In the leadup to the hearing, Republicans readied their trumped-up attacks against Khan and the agency she leads: a barely relevant memo from a conflicted ethics officer, a list of unfounded grievances from bitter former Commissioner Christine Wilson, and absurd defenses of Elon Musk’s lazy privacy practices at Twitter. But Khan emerged unscathed, and by the end, the Republicans had lost all their fire.

July 26, 2023
It’s Time For “Union Joe” To Prove Himself
If Biden wants to keep his nickname and the working class vote, he needs to start listening to the unions.

July 07, 2023 | Democracy Journal
RELEASE: Understanding How Budget Reforms Were Exploited To Drain Federal Agencies Can Help Americans Develop a Strategy to Fight Back.
Revolving Door Project’s Fatou Ndiaye published a piece in Democracy Journal outlining the staggering gap between how the appropriations process for federal agencies is supposed to work versus how it currently works. Understanding the difference can help Americans refine strategies to get our voices heard in Congress and shine light on overlooked contributors to chronic underfunding across the federal government. Such an examination is especially relevant as Congress appears poised for a series of fiscal nightmares this fall.

June 28, 2023 | Revolving Door Project Newsletter
Eighteen Months To Avoid Another X-Date
Earlier this month, Politico reported that after Biden secured his debt ceiling deal—a deal whose poison pills we’ll still be unpacking for some time to come—he went quiet on exploring options to permanently get rid of the debt ceiling.
This goes against what the president promised agitated members of his own party who urged him to take any manner of executive branch routes to resolve the crisis without capitulating to Republican demands: that it was his “hope and intention” to “find a rationale to take it to the courts to see whether or not the 14th Amendment is, in fact, something that would be able to stop it.” And it sets us up for another protracted, exhausting, damaging tête-à-tête at the edge of a fiscal cliff in just eighteen months.
June 02, 2023
Hack Watch: Larry Summers Thinks Starving Older Americans Serves A "Useful Function"
Summers’ evaluation of the deal President Biden struck with House Speaker McCarthy includes tepid support for work requirements.

May 26, 2023
RELEASE: Revolving Door Project Reacts to Biden’s Debt Ceiling Cave & the Media’s Incompetent Coverage
In response to the emergence of the structure of a potential deal between President Biden and Speaker McCarthy, Revolving Door Project Executive Director Jeff Hauser issued the following statement:
“There are three aspects to the substance and coverage of this debate that have been infuriating.”

May 17, 2023
Executive Branch Agencies That Protect Americans From Corporate Abuses Need Robust Funding, Not Cuts
With executive branch agencies under renewed attack as President Biden negotiates with the GOP, we revisit our research on government capacity.

May 10, 2023 | Revolving Door Project Newsletter
The GOP Budget Plan Would Ruin Millions of Lives
There are a lot of things you could say about the GOP’s proposed plan to reduce the deficit. But if we want to be more expansive than just calling it “batshit crazy” and washing our hands of the whole clown show, as we think Biden can and should, then we could point out that the GOP plan is an expression of profound hostility to the idea of a federal government that serves anyone besides war profiteers.
May 03, 2023 | Revolving Door Project Newsletter
On the Debt, Biden Has No Choice But To Make One
On Monday, Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen shortened the estimate of when the U.S. could default on its debt to as soon as June 1. We’re less than a month out from the so-called X-date: the day that the federal government runs out of cash. President Biden has invited House and Senate leadership to the White House to talk debt this coming Tuesday, with highly uncertain results.

April 19, 2023
KJ Boyle Andrea Beaty Emma Marsano
Anti-MonopolyConsumer ProtectionDepartment of JusticeFTCGovernment CapacityIndependent Agencies
To Reverse Decades Of Neglect, Antitrust Agencies Need Robust Budgets
The FTC and the DOJ are still dealing with a deluge of corporate mergers, and still only have capabilities to challenge a handful of those actions each year. Restoring competition in the U.S. economy will require much more than slight increases in funding — these government agencies need monumental budgets to take on entrenched monopolies that have flourished with decades of lax enforcement.
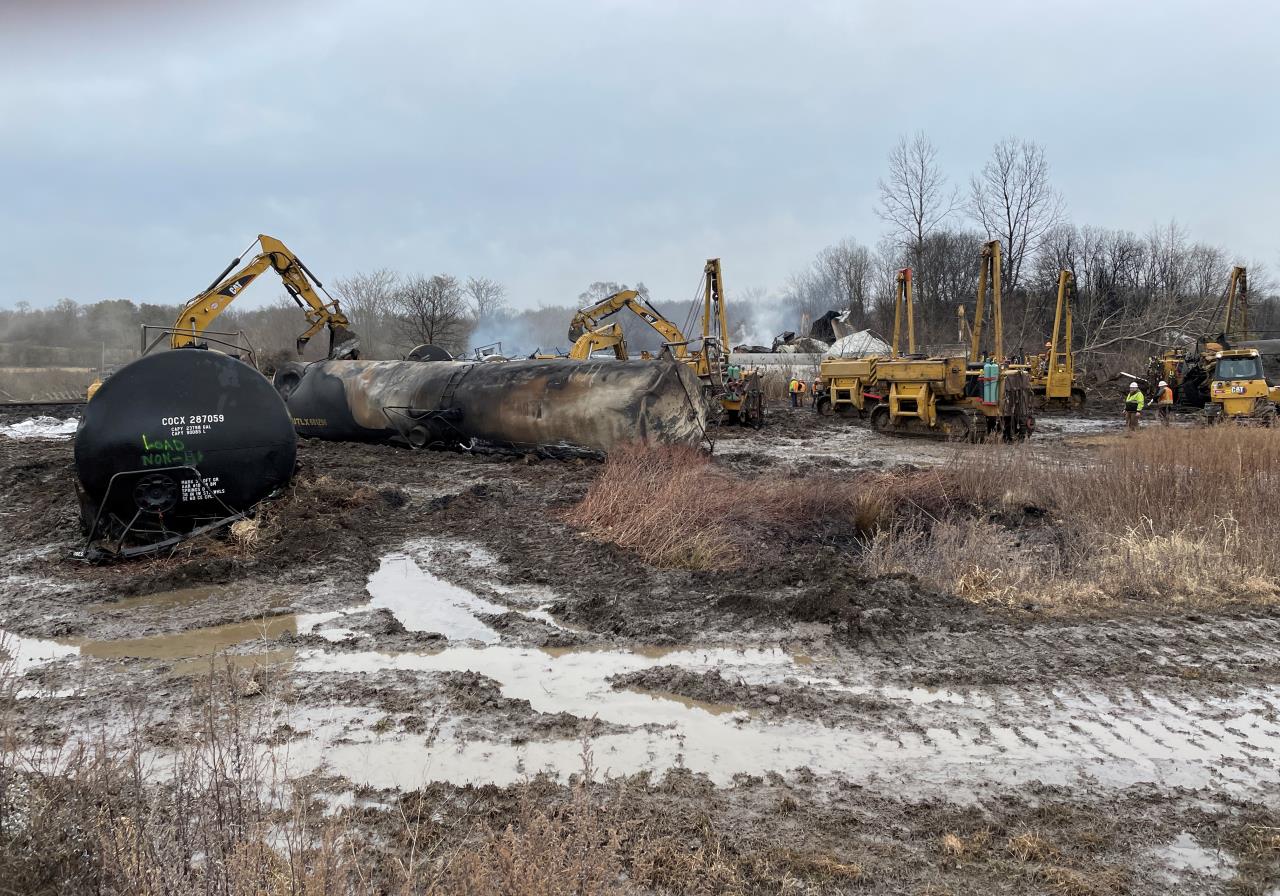

March 01, 2023 | The American Prospect
Op-Ed Climate and EnvironmentConsumer ProtectionCorporate CrackdownExecutive BranchGovernanceGovernment Capacity
Calling Deficit Squawks’ Bluff on Environmental Enforcement
A 38-car train wreck. Toxic chemicals seeping into water and soil, and a black plume rising in the sky. Sick people, sick pets. As the Prospect’s Jarod Facundo wrote last week, the national spotlight remains fixed on the ecological consequences of the February 3 derailment of a Norfolk Southern train carrying hazardous chemicals in East Palestine, Ohio.
In the context of this ecological disaster, arguing for a reduced budget for federal investigators, air and water quality testing, and programs that hold polluting corporations accountable for proper cleanup and restitution is sheer madness. But that’s exactly what the current right-wing push for massive government spending cuts in the name of deficit reduction would entail.
